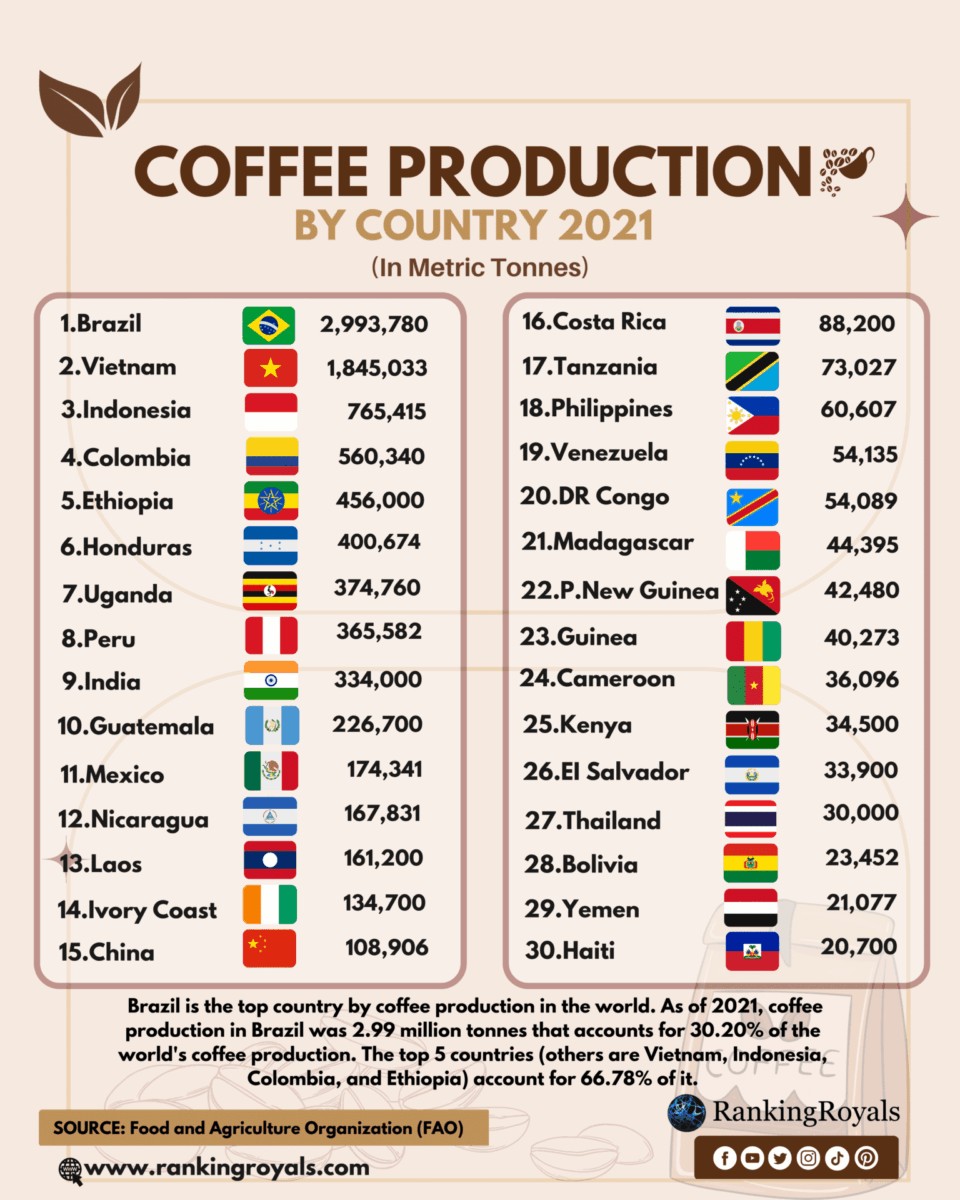
Coffee has taken center stage in the global market, with three countries standing out as the giants of coffee producing. Brazil, the unchallenged leader, dominates the industry, thanks to its ideal climate and vast plantations. Following closely, Vietnam showcases remarkable growth, rapidly increasing its share in the market. Meanwhile, Colombia captivates coffee lovers with its rich Arabica beans, establishing a unique identity. As the demand for coffee surges worldwide, understanding the dynamics of these powerhouse nations becomes crucial in addressing both economic impacts and sustainability challenges.
Introduction to Coffee Production
Coffee producing is more than just an agricultural activity; it is a global phenomenon that fuels economies and cultures alike. Around the world, billions of people savor this caffeinated beverage daily, making coffee one of the most popular commodities.
In 2022 alone, worldwide coffee production reached approximately 175 million 60-kilogram bags, with projections indicating continual growth. Here’s a quick look at the top coffee producing countries:
| Rank | Country | Production (Million Bags) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brazil | 60.3 |
| 2 | Vietnam | 29.5 |
| 3 | Colombia | 14.2 |
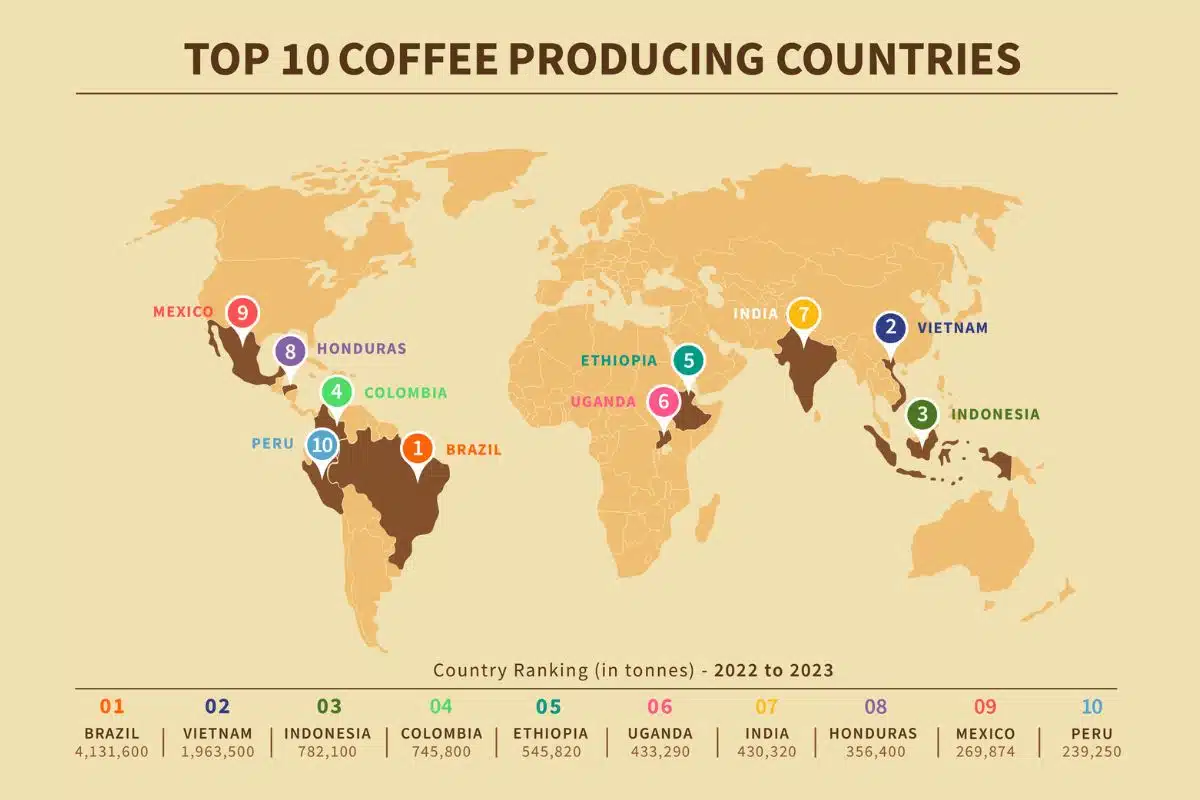
As shown in the table, Brazil stands out as the unrivaled leader in coffee producing, contributing over one-third of the global supply. Following Brazil, Vietnam has made significant strides, particularly in robusta coffee varieties. Meanwhile, Colombia, known for its exquisite Arabica beans, completes the top three.
The coffee producing landscape showcases diverse climates and altitudes, defining flavor profiles and cultivation methods. With advancements in technology and varying consumer preferences, the coffee industry continues to evolve. As we delve deeper into each country’s unique contributions, we begin to appreciate the intricate world of coffee production and its economic significance.
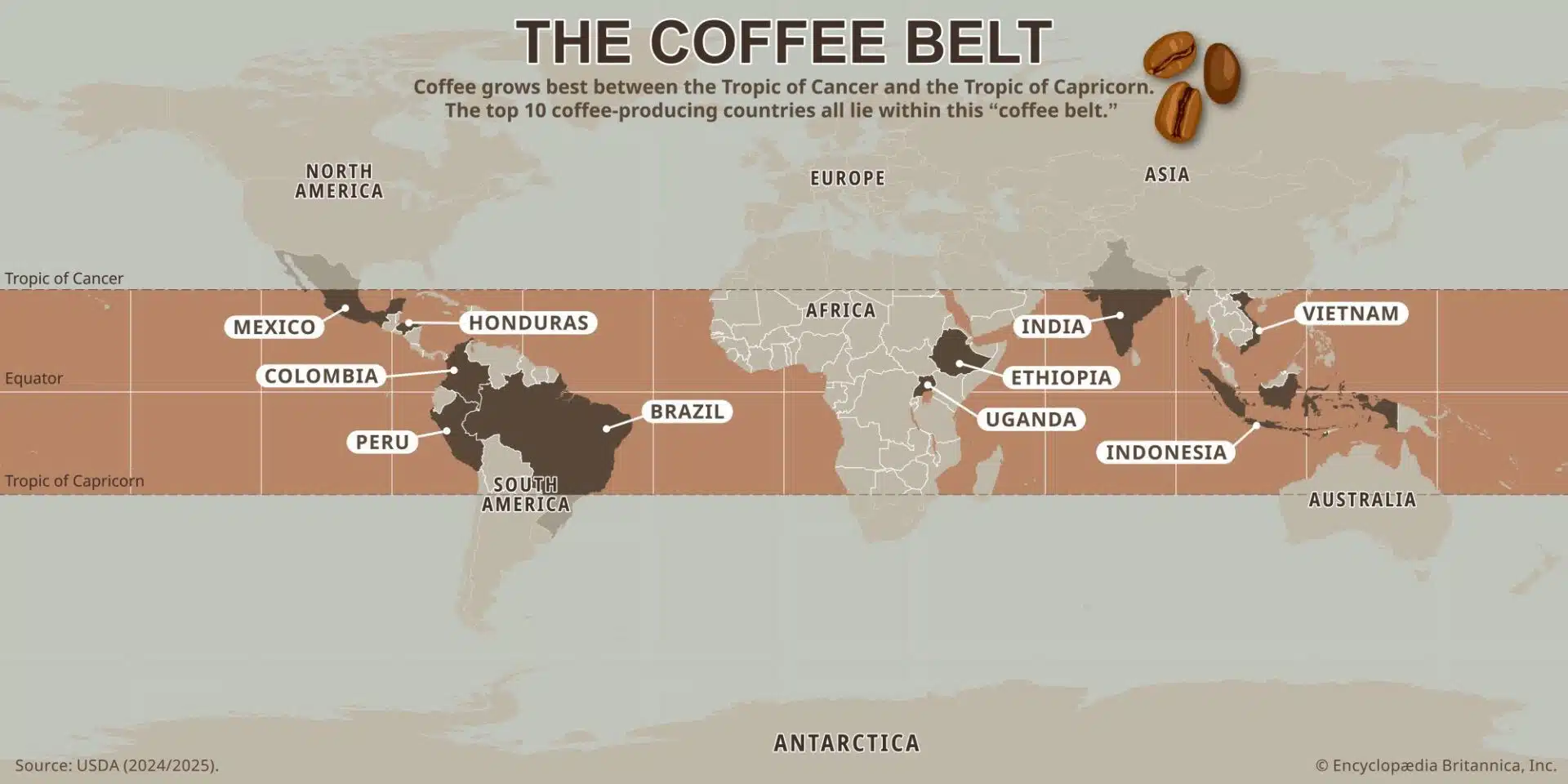
Brazil: The Unrivaled Leader
Brazil continues to hold its position as the world’s largest coffee producing nation, contributing approximately 37% of global coffee supply. This immense output stems from a combination of favorable climate conditions, extensive plantations, and innovative farming techniques.
Key aspects of Brazil’s coffee production include:
- Diverse Varieties: Brazil mainly produces two types of coffee:
- Arabica: Known for its sweet, complex flavors.
- Robusta: Offers a stronger, more bitter taste and accounts for about 30% of Brazil’s total coffee production.
- Geographic Advantage: Brazil’s vast landscape allows for cultivation in several regions, including Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Espírito Santo, each producing unique coffee profiles.
- Economies of Scale: With large-scale operations, Brazilian coffee producers benefit from lower production costs, making their coffee competitive in international markets.
Comparison of Coffee Production Volume (2022)
| Country | Coffee Production (Million 60kg Bags) | Percentage of Global Production |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 63.4 | 37% |
| Vietnam | 30.8 | 18% |
| Colombia | 14.2 | 8% |
The ongoing commitment to innovation and sustainability ensures Brazil remains a dominant force in coffee producing. Consequently, as global demand rises, Brazil is poised to maintain its lead, industry experts suggest.
Vietnam: A Growing Powerhouse
Vietnam has rapidly emerged as a significant player in the global coffee producing landscape. Once mainly known for its rice production, Vietnam now stands as the second-largest coffee producer in the world, trailing only behind Brazil. This transformation has been remarkable, considering that the country only began cultivating coffee in the late 19th century.
Key Highlights of Vietnam’s Coffee Production:
- Robusta Dominance: Approximately 95% of Vietnam’s coffee is Robusta, which caters to the growing demand for espresso blends and instant coffee. In fact, the Robusta variety thrives well in Vietnam’s diverse climates.
- Export Growth: With substantial export growth over recent years, Vietnam’s coffee exports reached 1.8 million tons in 2020, generating over $3 billion in revenue. This upward trajectory positions Vietnam as a powerhouse in the global market.
- Cultural Significance: Coffee culture is deeply embedded in Vietnamese society. Traditional methods of brewing coffee with a drip filter, known as “phin,” showcase the rich heritage while increasing local consumption.
Comparative Table: Coffee Production of Key Countries
| Country | Coffee Type | Annual Production (Million Tons) | Export Revenue (Billion USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Arabica and Robusta | 3.0 | 5.0 |
| Vietnam | Robusta | 1.8 | 3.0 |
| Colombia | Arabica | 0.8 | 1.5 |
In summary, Vietnam’s robust coffee producing sector is marked by innovation, efficiency, and a unique cultural touch. As coffee demand continues to rise, Vietnam is poised to solidify its position as a global leader in coffee production.
Colombia: The Heart of Arabica Coffee
Colombia firmly establishes itself as the heart of Arabica coffee, known for its high-quality beans and unique flavor profile. In fact, Colombian coffee boasts a significant global presence, making it one of the top coffee producing countries worldwide.
Key Features of Colombian Coffee:
- Distinct Flavor: Colombian Arabica coffee features a smooth, mild taste with natural sweetness and hints of caramel.
- Ideal Climate: The country’s diverse geography and equatorial climate provide optimal growing conditions, allowing for year-round harvests.
- Varied Altitude: Colombian coffee farms often exist at altitudes ranging from 1,200 to 2,000 meters, leading to denser, more flavorful beans.
Comparison of Coffee Production
| Country | Type of Coffee | Annual Production (in metric tons) |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Robusta & Arabica | 3,000,000 |
| Vietnam | Robusta | 1,600,000 |
| Colombia | Arabica | 900,000 |
In summary, Colombia excels in coffee producing primarily due to its commitment to quality and sustainable farming practices. The reputation of Colombian Arabica coffee continues to enhance its position in international markets, ensuring that this country remains synonymous with top-tier coffee. As demand for high-quality coffee grows, Colombia’s role as the heart of Arabica coffee becomes even more pivotal.
Impact of Climate on Coffee Production
Climate plays a crucial role in coffee producing, significantly influencing both the quality and quantity of coffee harvests. Various factors, including temperature, humidity, and rainfall patterns, directly affect where coffee can thrive. Here’s a look at how climate impacts coffee production:
- Temperature Sensitivity: Coffee plants, particularly Arabica, flourish in specific temperature ranges (60°F to 70°F). Extreme heat can lead to reduced yields and compromised flavor profiles.
- Rainfall Dependency: Coffee requires consistent rainfall; however, both excess and insufficient precipitation poses risks. Beneficial rainfall during growth contrasts sharply with the detrimental effects of drought during harvest.
- Pests and Diseases: Climate change exacerbates the spread of pests and diseases in coffee plants. Warmer temperatures have increased the prevalence of pests like the coffee borer beetle, which can devastate crops.
| Climate Factor | Optimal Condition | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 60°F – 70°F | Heat stress reduces yield |
| Rainfall | 40 – 100 inches annually | Drought results in lower quality |
| Humidity | 60% – 80% | High humidity can increase diseases |
As global climate patterns shift, coffee producing regions must adapt by implementing sustainable practices and diversifying coffee varieties to ensure a robust future for this beloved beverage.
Economic Significance of Coffee Exports
Coffee producing nations play a critical role in the global economy, with coffee exports serving as a vital source of income for millions. For many developing countries, coffee is not just a beverage; it represents an economic lifeline. Consider these impactful statistics:
- Revenue Generation: Coffee contributes significantly to the GDP of top-producing countries. For instance, Brazil’s coffee industry generates billions in revenue, making it a cornerstone of its economy.
- Employment: The coffee sector employs millions worldwide, from farm workers to baristas, stabilizing livelihoods and fostering community development.
- Export Dependence: Countries like Colombia and Vietnam rely heavily on coffee exports, with a substantial percentage of their agricultural export revenue derived from this single crop.
Comparison of Major Coffee Exporters:
| Country | Coffee Production (metric tons) | Export Revenue (USD) | % of Total Exports |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 3,000,000 | 5 billion | 20% |
| Vietnam | 1,700,000 | 3.6 billion | 15% |
| Colombia | 800,000 | 2 billion | 12% |
In summary, the economic significance of coffee exports cannot be understated. The coffee producing industry serves as a vital engine for growth, fostering development both locally and globally. As demand for coffee continues to rise, so does the importance of sustaining these key coffee-producing economies.
Challenges Facing Coffee Producers
Despite the robust growth in coffee producing sectors globally, producers face a myriad of challenges that threaten their livelihoods and the sustainability of this beloved beverage. Here are the key issues impacting coffee producers today:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns directly affect coffee yields. Heat stress reduces the quality of coffee beans, while fluctuations in climate can lead to pest and disease outbreaks.
- Economic Volatility: Coffee prices fluctuate significantly in the global market. This volatility leaves small-scale farmers vulnerable, as many operate on thin margins. A drop in prices can push farmers into poverty, jeopardizing their ability to invest in sustainable practices.
- Pest and Disease Threats: Coffee crops are susceptible to various diseases, such as coffee leaf rust and coffee borer beetle infestations. Managing these requires considerable resources, and smallholders often lack access to effective treatments.
- Labor Shortages: As urbanization rises, fewer individuals are willing to work in the coffee fields. This shortage increases labor costs and poses a challenge to coffee producing regions, particularly those dependent on manual harvesting.
- Sustainability Issues: Environmental concerns arise from conventional farming methods, leading to soil degradation and water contamination. Transitioning to sustainable practices requires investment and education, which can be hard to come by for small producers.
In conclusion, while coffee producing remains a vital economic driver, addressing these challenges will require concerted efforts from governments, organizations, and the coffee community.
Future Trends in Coffee Production
As the world continues to evolve, so do the practices and technologies in coffee producing countries. Here are key trends shaping the future of coffee production:
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Increasing consumer awareness about environmental impact is pushing producers towards organic and ethical farming methods. Many coffee producing countries are adopting techniques like agroforestry, which promotes biodiversity and reduces deforestation.
- Climate Resilience: With climate change threatening traditional coffee farming, producers are experimenting with climate-resilient coffee varieties. For instance, hybrids that withstand extreme temperatures and pests will gain prominence in coffee producing regions.
- Technology Integration: Innovations such as precision agriculture and data analytics are revolutionizing coffee cultivation. Coffee farmers are utilizing drones and sensors to monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and improve yield.
- E-commerce Growth: As demand for specialty coffee rises, online sales are becoming increasingly important. Consumers can now access unique blends from various coffee producing countries directly, enhancing market access for smaller producers.
- Focus on Quality over Quantity: The global market is shifting towards high-quality coffee. Producers are concentrating on premium grade beans, leading to better prices and more sustainable income for farmers.
These trends indicate a promising future for coffee producing countries, ultimately enhancing both the quality of coffee and the livelihoods of those who cultivate it.
Sustainability in Coffee Farming
As the demand for coffee surges globally, sustainability in coffee producing becomes increasingly essential. The coffee industry faces significant environmental and social challenges that prompt both producers and consumers to prioritize sustainable practices. Here are key aspects contributing to sustainable coffee farming:
- Biodiversity: Coffee producers are adopting agroforestry systems that promote the growth of diverse plant species. This practice not only enhances soil health but also supports local wildlife.
- Water Conservation: Sustainable coffee farms implement efficient irrigation techniques and rainwater harvesting to minimize water waste. By using shade-grown coffee methods, they also reduce water evaporation.
- Fair Trade Practices: Many coffee producers participate in fair trade certification, ensuring equitable prices for farmers. This commitment not only supports local economies but also promotes ethical labor practices.
- Organic Farming: Increasingly, coffee producers are transitioning to organic farming methods that eliminate synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, fostering healthier ecosystems.
To illustrate these concepts, consider the comparison of conventional vs. sustainable coffee farming:
| Aspect | Conventional Farming | Sustainable Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Usage | High | Low |
| Water Consumption | High | Moderate |
| Biodiversity Support | Low | High |
| Economic Benefits | Short-term gains | Long-term sustainability |
In conclusion, the shift towards sustainable practices in coffee producing not only addresses environmental concerns but also secures the future of coffee for generations to come.
Conclusion: The Coffee Landscape Ahead
As the global demand for coffee continues to flourish, the coffee producing landscape faces an array of challenges and opportunities. With the top producers—Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia—steering the market, the industry must address issues such as climate change, sustainability, and market fluctuations.
Key Insights:
- Adapting to Climate Change: Coffee producers must innovate in cultivation techniques to mitigate the adverse effects of rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns. This involves investing in resilient crop varieties and sustainable farming practices.
- Emerging Markets: Countries like Ethiopia and Honduras are gaining traction, adding diversity to the coffee producing sector. These nations may provide new opportunities for specialty coffee niches, appealing to discerning consumers.
- Sustainability Emphasis: With increasing consumer awareness about provenance and sustainability, coffee producers that champion eco-friendly practices stand to benefit. This shift could redefine market dynamics and drive innovation.
In summary, the future of coffee producing hinges on adaptability, sustainability, and the ability to meet evolving consumer preferences. By navigating these challenges thoughtfully, coffee producers can not only maintain their positions in the market but also pave the way for a vibrant and sustainable coffee industry in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which countries are the top coffee producers in the world?
The three largest coffee producing countries in the world are Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia. Brazil, the frontrunner, produces a significant portion of the world’s coffee supply due to its favorable climate and diverse coffee plantations. Vietnam ranks second, with a focus on robusta beans, which have gained popularity in the global market. Colombia, known for its high-quality arabica beans, is a key player thanks to its unique geography that enhances flavor profiles.
What types of coffee do these countries produce?
Brazil predominantly produces arabica coffee, which is known for its smooth, sweet flavor and less acidity. However, it also grows robusta beans, particularly in specific regions. Vietnam, on the other hand, is renowned for its robusta beans, which tend to be stronger and more bitter compared to arabica. Colombia primarily focuses on high-quality arabica coffee, often recognized for its balanced flavor and aroma, making it highly sought after by coffee connoisseurs.
How does climate affect coffee production in these countries?
Climate plays a crucial role in coffee cultivation, particularly in Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia. Brazil benefits from a tropical climate with suitable altitudes for coffee growing, which results in abundant yields. Vietnam has a diverse climate with different regions contributing to coffee production, especially in the central highlands. Colombia’s unique high-altitude conditions provide excellent drainage and temperature control, producing some of the best arabica coffee in the world, resulting in rich flavors and quality.
What impact does coffee production have on the economies of these countries?
Coffee production is a vital economic driver in Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia, supporting millions of farmers and workers. In Brazil, coffee is one of the main agricultural exports, significantly contributing to its GDP. For Vietnam, coffee is a cornerstone of the economy, securing its position as a leading coffee exporter. In Colombia, coffee not only represents a major export but also fosters rural development and jobs, with coffee farms often serving as vital community hubs.
What are the challenges facing coffee producers in these countries?
Coffee producers in Brazil, Vietnam, and Colombia face several challenges, including climate change, which affects coffee yields and quality due to extreme weather patterns. Additionally, pests and diseases such as coffee leaf rust threaten crops. Economic fluctuations, fluctuating prices, and the need for sustainable practices also pose ongoing pressures for farmers. These challenges push the industry to innovate constantly, from adopting new agricultural practices to exploring alternative markets.